Battered by Hurricane Idalia last year, Florida village ponders future as hurricane season begins

Lisa Bregenzer’s waterfront home was her "little slice of heaven." She watched sunsets and migrating birds from the porch, the Gulf of Mexico in the distance. There, she felt close to God and her late father.
When Hurricane Idalia tore through Florida in late August, Bregenzer lost everything in the northwest fishing village of Horseshoe Beach. For months, she and her husband slept where they could with friends, neighbors and family: in Tennessee, Georgia, West Virginia, eastern Florida.
For nearly 11 months, Bregenzer felt she was no better off than after the storm.
“I’m spent. I’m tired. I’m weak. And I’m weary,” Bregenzer said in May inside a temporary, state-issued camper she lives in several miles away. “Everyday I am reminded of the storm."
Almost a year later, many people in Horseshoe are asking themselves: Do I sell and move? Should I buy a recreational vehicle to live in on my property? Do I have the means to rebuild on stilts, as code requires? As they ask these questions, U.S. officials predict this year's hurricane season in Florida will be busier than usual.
Coastal climate impacts
In the U.S., more than 128 million people – nearly 40% of the nation’s population – live in coastal counties along the Atlantic, Pacific and Arctic oceans, as well as the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. These seaside communities produce $10 trillion in goods and services annually, employ 54.6 million people, and pay $4 trillion in wages, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
To live along the coast in a time of climate change is to contend with increasing vulnerabilities. Seas are rising and warming up, eroding coastlines, intensifying storms and making floods a more frequent occurrence.
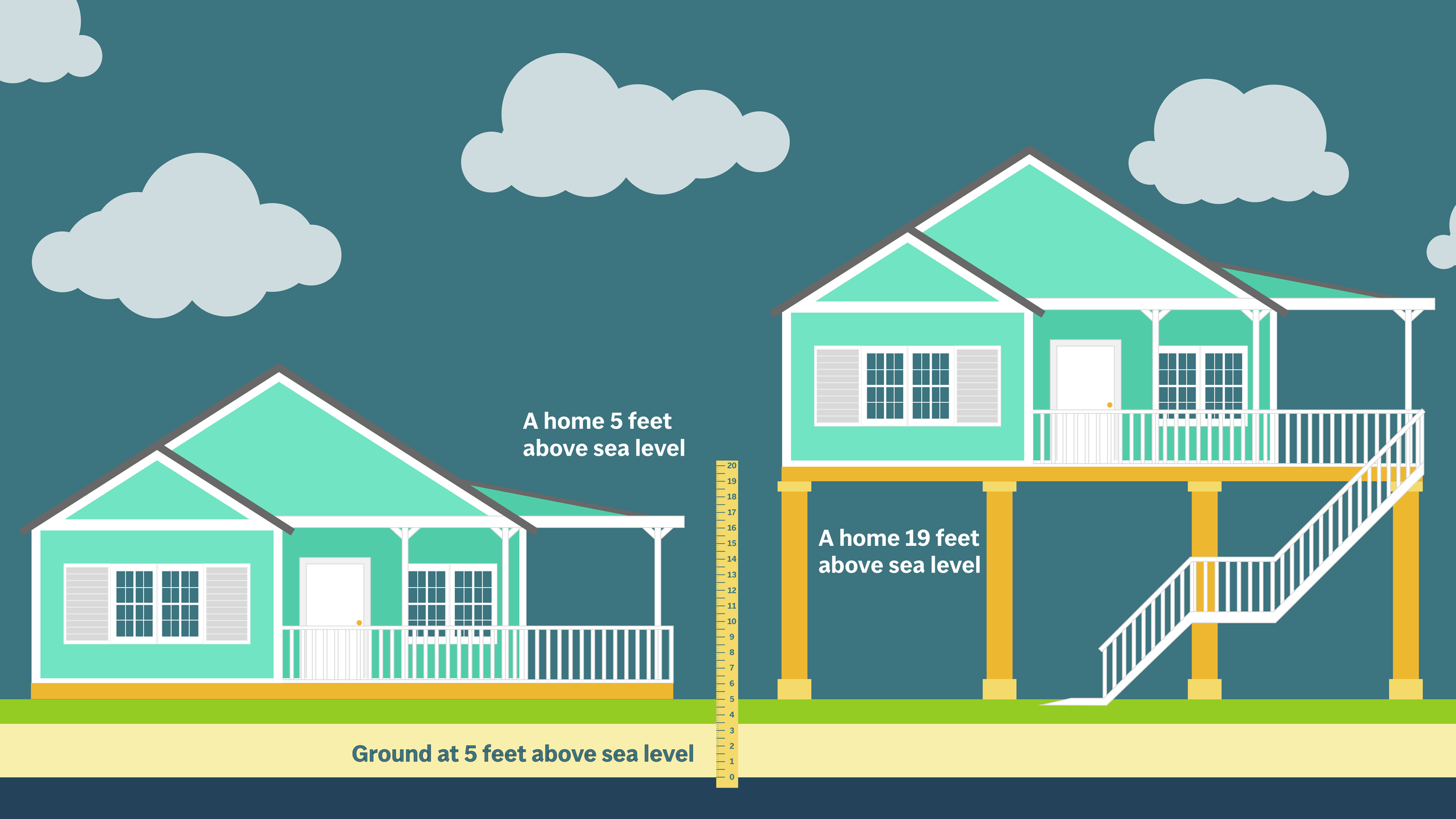
In Horseshoe, those who lost homes to Idalia have few options. They can either rebuild on pricey stilts — up to 19 feet (5.8 meters) above sea level as required for buildings closest to water — or live in RVs they can move from a hurricane's path.
Powerful hurricanes mean homes must be built higher, but it’s costly
Located 70 miles (113 kilometers) west of Gainesville, Horseshoe is a quiet town in Dixie County. Residents zip around in golf carts and move with the days' rhythms — lounging when it's hottest, fishing when the tide is right, watching sunsets, beers in hand. Less than 200 full-time residents, both recent retirees and long-timers, as well as weekenders and seasonal tourists, are spread over an area about three-quarters of a mile long and wide. There is one church, one firehouse and one restaurant. There is no gas station or grocery store, and only one road goes in and out.
Horseshoe residents say they are proud of strong community bonds and sunsets that paint the sky brilliant hues. Homes approaching $1 million are interspersed with some as low as $50,000. Historically, it's a place where a blue collar worker could live by the sea.
Many residents are still reeling from last summer’s Category 3 storm that pummeled homes, businesses and other infrastructure, leaving debris and rubble in its wake. Recovery for some has been long and slow. Elevated homes withstood severe damage. Homes with little elevation were destroyed. Many weren't insured, and those who did have flood insurance were not covered for repairs from wind-driven water. Scientists have said that Gulf waters warmed by climate change helped Idalia rapidly intensify
Today, the signs of destruction remain. A house lies flat like a pancake. Abandoned homes with shattered windows – some boarded up with wood – stand askew. Inside, washers and driers are turned on their sides. A tattered American flag flaps where a house was swept away and flags reading “Horseshoe Strong” hang from balconies, made after Idalia by a local who lost her business.
Storms reshape Horseshoe
People talk about keeping Horseshoe unchanged, but before Idalia storms had begun reshaping the town's character and landscape.
Hurricane Hermine in 2016, and before that, the so-called Storm of the Century in 1993, caused widespread damage. People sold their properties. Some houses went up on stilts. In 1993, Tina Brotherton lost her marina and the cafe next door, and had to replace the floors and beds at her inn. Most of the damaged buildings were on the waterfront, she recalled.
Idalia dealt another blow.
Brotherton, 88, said she doesn’t plan to rebuild this time. Her business, Tina’s Dockside Inn, was completely destroyed, as was her home that she planned to put on the market days before the storm. She says she is tired and it's expensive to rebuild.
“Once I got all my cats out, I don’t care to go back,” she said inside her home a couple of miles away, where she lives with her son and more than a dozen cats. “There’s nothing there for me anymore.”
Long road to recovery
By midcentury, more than 48,000 properties could be below the high tide lines, mostly in Louisiana, Florida and Texas, according to a 2022 study by Climate Central.
While Horseshoe residents say they know storms and flooding will continue, it's hard to think about that when trying to survive the present.
Eileen Lilley, 75, is living in a camper after 5 feet (1.5 meters) of water damaged her home. On a recent day, she spoke of her late husband and missing the screened porch where she liked to paint. Despite the longing, she feels safe knowing her mobile home can be moved when another hurricane strikes.
“It’s better for me at my age to get somebody who can pull me out of here and move me to another area,” she said, while at her side snoozed Katy the cat and Kelly the dog laid at her feet.
Some residents are waiting to know if they qualify for state or federal loans and grants to help them rebuild. Mayor Jeff Williams said insuring new property will also be cost prohibitive for many. “In a town when you’re in a flood zone, you pay the highest rate,” he said. “And the rate of insurance over the last two to three years has just skyrocketed.”
All this added to Bregenzer's anxiety. To rebuild they needed financial help. Her husband had a stroke and back surgery years ago, and medical bills and income loss sapped their savings. She's grateful to have a roof over her head.
“It's humbling,” she said.
They want to be homeowners again, she said while sitting inside her camper, tears in her eyes. To have a house to show for their lives' work. For nearly a year, she didn't know if that would happen or when. And she wondered: is it even worth it?
Then just last week, Bregenzer finally found hope. Her family was approved for a program that will help them build a new home. If all goes as planned, they'll move into an stilted two-bedroom house on their lot by year's end.
“After 11 months of what seemingly felt and appeared to be a nightmare, I just,” she said over the phone in July, her voice trailing off. “I lack words.”
The Associated Press receives support from the Walton Family Foundation for coverage of water and environmental policy. The AP is solely responsible for all content. For all of AP’s environmental coverage, visit https://apnews.com/hub/climate-and-environment
Text from AP News story, Battered by Hurricane Idalia last year, Florida village ponders future as hurricane season begins, by Dorany Pineda and Rebecca Blackwell.